14 KiB
Evaluations
The Llama Stack Evaluation flow allows you to run evaluations on your GenAI application datasets or pre-registered benchmarks.
We introduce a set of APIs in Llama Stack for supporting running evaluations of LLM applications.
/datasetio+/datasetsAPI/scoring+/scoring_functionsAPI/eval+/eval_tasksAPI
This guide goes over the sets of APIs and developer experience flow of using Llama Stack to run evaluations for different use cases. Checkout our Colab notebook on working examples with evaluations here.
Evaluation Concepts
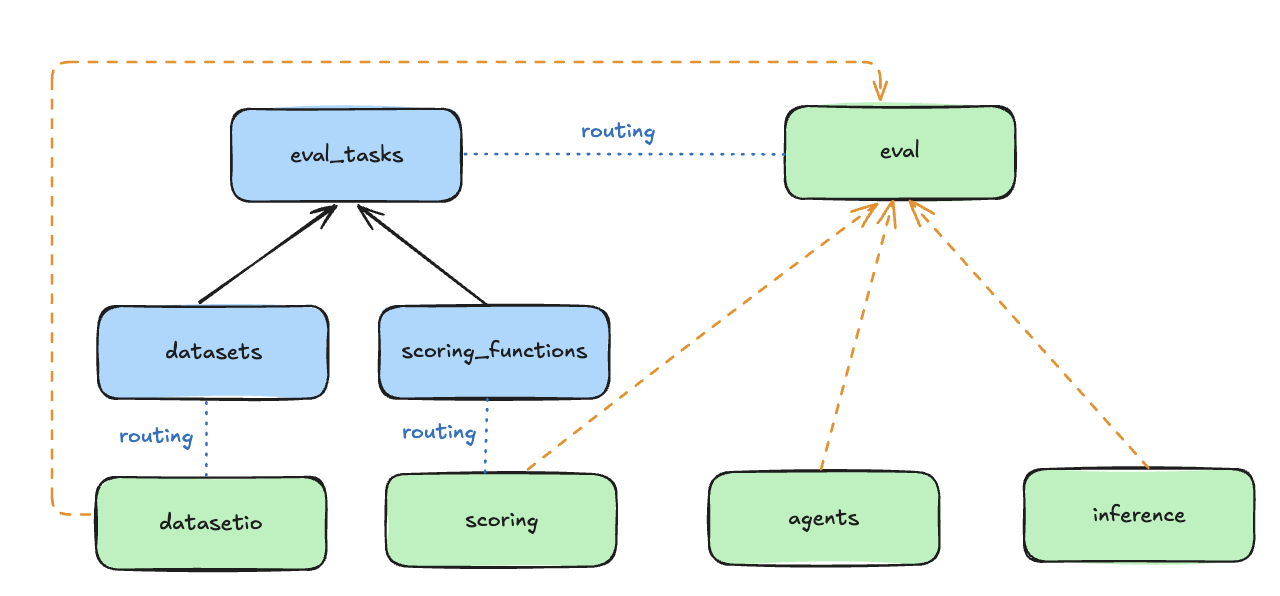
The Evaluation APIs are associated with a set of Resources as shown in the following diagram. Please visit the Resources section in our Core Concepts guide for better high-level understanding.
- DatasetIO: defines interface with datasets and data loaders.
- Associated with
Datasetresource.
- Associated with
- Scoring: evaluate outputs of the system.
- Associated with
ScoringFunctionresource. We provide a suite of out-of-the box scoring functions and also the ability for you to add custom evaluators. These scoring functions are the core part of defining an evaluation task to output evaluation metrics.
- Associated with
- Eval: generate outputs (via Inference or Agents) and perform scoring.
- Associated with
EvalTaskresource.
- Associated with
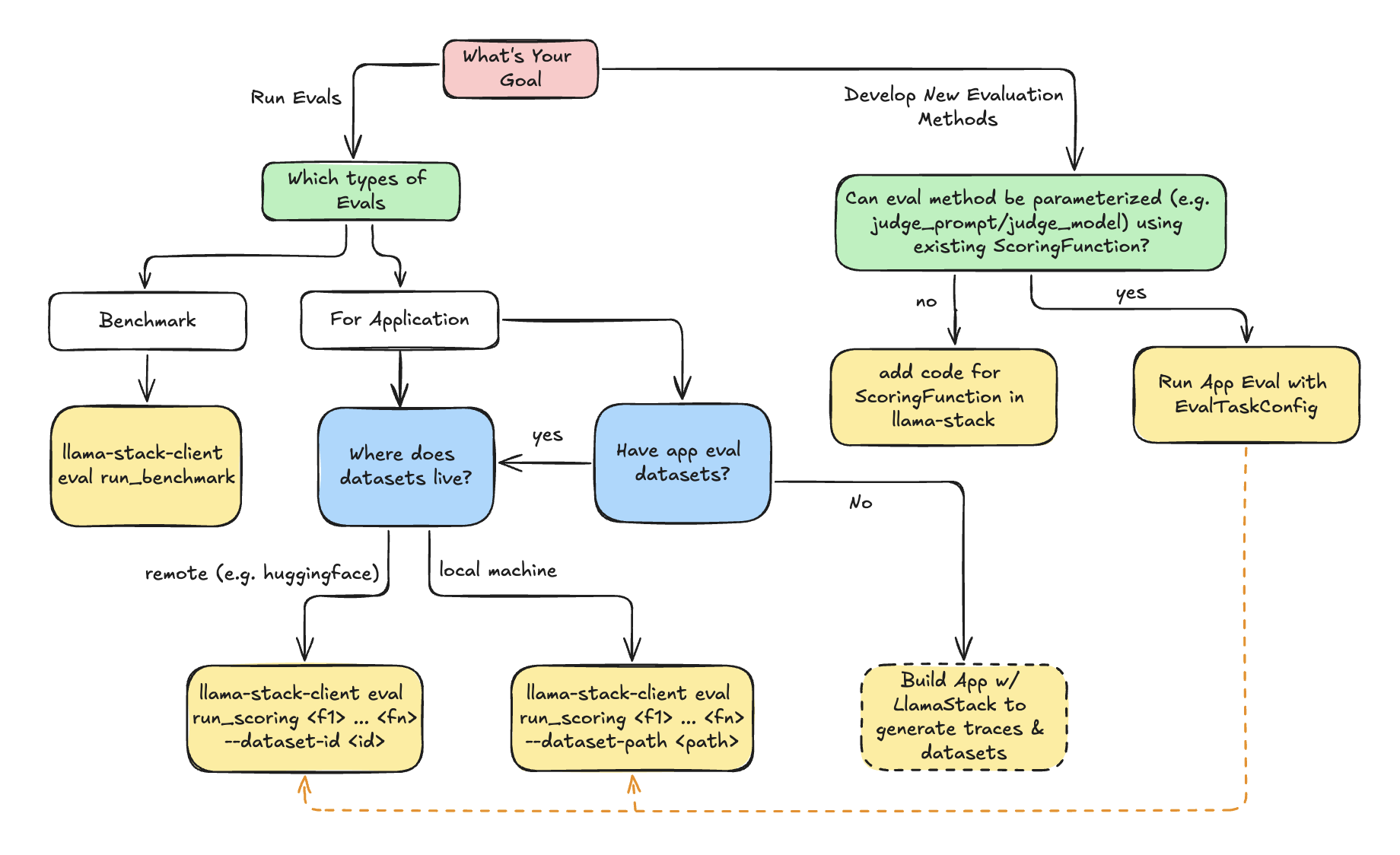
Use the following decision tree to decide how to use LlamaStack Evaluation flow.
:class: tip
- **Benchmark Evaluation** is a well-defined eval-task consisting of `dataset` and `scoring_function`. The generation (inference or agent) will be done as part of evaluation.
- **Application Evaluation** assumes users already have app inputs & generated outputs. Evaluation will purely focus on scoring the generated outputs via scoring functions (e.g. LLM-as-judge).
Evaluation Examples Walkthrough
It is best to open this notebook in Colab to follow along with the examples.
1. Open Benchmark Model Evaluation
This first example walks you through how to evaluate a model candidate served by Llama Stack on open benchmarks. We will use the following benchmark:
- MMMU (A Massive Multi-discipline Multimodal Understanding and Reasoning Benchmark for Expert AGI)]: Benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models.
- SimpleQA: Benchmark designed to access models to answer short, fact-seeking questions.
1.1 Running MMMU
- We will use a pre-processed MMMU dataset from llamastack/mmmu. The preprocessing code is shown in this GitHub Gist. The dataset is obtained by transforming the original MMMU/MMMU dataset into correct format by
inference/chat-completionAPI.
import datasets
ds = datasets.load_dataset(path="llamastack/mmmu", name="Agriculture", split="dev")
ds = ds.select_columns(["chat_completion_input", "input_query", "expected_answer"])
eval_rows = ds.to_pandas().to_dict(orient="records")
- Next, we will run evaluation on an model candidate, we will need to:
- Define a system prompt
- Define an EvalCandidate
- Run evaluate on the dataset
SYSTEM_PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """
You are an expert in Agriculture whose job is to answer questions from the user using images.
First, reason about the correct answer.
Then write the answer in the following format where X is exactly one of A,B,C,D:
Answer: X
Make sure X is one of A,B,C,D.
If you are uncertain of the correct answer, guess the most likely one.
"""
system_message = {
"role": "system",
"content": SYSTEM_PROMPT_TEMPLATE,
}
client.eval_tasks.register(
eval_task_id="meta-reference::mmmu",
dataset_id=f"mmmu-{subset}-{split}",
scoring_functions=["basic::regex_parser_multiple_choice_answer"],
)
response = client.eval.evaluate_rows(
task_id="meta-reference::mmmu",
input_rows=eval_rows,
scoring_functions=["basic::regex_parser_multiple_choice_answer"],
task_config={
"type": "benchmark",
"eval_candidate": {
"type": "model",
"model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-90B-Vision-Instruct",
"sampling_params": {
"strategy": {
"type": "greedy",
},
"max_tokens": 4096,
"repeat_penalty": 1.0,
},
"system_message": system_message,
},
},
)
1.2. Running SimpleQA
- We will use a pre-processed SimpleQA dataset from llamastack/evals which is obtained by transforming the input query into correct format accepted by
inference/chat-completionAPI. - Since we will be using this same dataset in our next example for Agentic evaluation, we will register it using the
/datasetsAPI, and interact with it through/datasetioAPI.
simpleqa_dataset_id = "huggingface::simpleqa"
_ = client.datasets.register(
dataset_id=simpleqa_dataset_id,
provider_id="huggingface",
url={"uri": "https://huggingface.co/datasets/llamastack/evals"},
metadata={
"path": "llamastack/evals",
"name": "evals__simpleqa",
"split": "train",
},
dataset_schema={
"input_query": {"type": "string"},
"expected_answer": {"type": "string"},
"chat_completion_input": {"type": "chat_completion_input"},
},
)
eval_rows = client.datasetio.get_rows_paginated(
dataset_id=simpleqa_dataset_id,
rows_in_page=5,
)
client.eval_tasks.register(
eval_task_id="meta-reference::simpleqa",
dataset_id=simpleqa_dataset_id,
scoring_functions=["llm-as-judge::405b-simpleqa"],
)
response = client.eval.evaluate_rows(
task_id="meta-reference::simpleqa",
input_rows=eval_rows.rows,
scoring_functions=["llm-as-judge::405b-simpleqa"],
task_config={
"type": "benchmark",
"eval_candidate": {
"type": "model",
"model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-90B-Vision-Instruct",
"sampling_params": {
"strategy": {
"type": "greedy",
},
"max_tokens": 4096,
"repeat_penalty": 1.0,
},
},
},
)
2. Agentic Evaluation
- In this example, we will demonstrate how to evaluate a agent candidate served by Llama Stack via
/agentAPI. - We will continue to use the SimpleQA dataset we used in previous example.
- Instead of running evaluation on model, we will run the evaluation on a Search Agent with access to search tool. We will define our agent evaluation candidate through
AgentConfig.
agent_config = {
"model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct",
"instructions": "You are a helpful assistant",
"sampling_params": {
"strategy": {
"type": "greedy",
},
},
"tools": [
{
"type": "brave_search",
"engine": "tavily",
"api_key": userdata.get("TAVILY_SEARCH_API_KEY"),
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto",
"tool_prompt_format": "json",
"input_shields": [],
"output_shields": [],
"enable_session_persistence": False,
}
response = client.eval.evaluate_rows(
task_id="meta-reference::simpleqa",
input_rows=eval_rows.rows,
scoring_functions=["llm-as-judge::405b-simpleqa"],
task_config={
"type": "benchmark",
"eval_candidate": {
"type": "agent",
"config": agent_config,
},
},
)
3. Agentic Application Dataset Scoring
-
Llama Stack offers a library of scoring functions and the
/scoringAPI, allowing you to run evaluations on your pre-annotated AI application datasets. -
In this example, we will work with an example RAG dataset and couple of scoring functions for evaluation.
llm-as-judge::base: LLM-As-Judge with custom judge prompt & model.braintrust::factuality: Factuality scorer from braintrust.basic::subset_of: Basic checking if generated answer is a subset of expected answer.
-
Please checkout our Llama Stack Playground for an interactive interface to upload datasets and run scorings.
judge_model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8"
JUDGE_PROMPT = """
Given a QUESTION and GENERATED_RESPONSE and EXPECTED_RESPONSE.
Compare the factual content of the GENERATED_RESPONSE with the EXPECTED_RESPONSE. Ignore any differences in style, grammar, or punctuation.
The GENERATED_RESPONSE may either be a subset or superset of the EXPECTED_RESPONSE, or it may conflict with it. Determine which case applies. Answer the question by selecting one of the following options:
(A) The GENERATED_RESPONSE is a subset of the EXPECTED_RESPONSE and is fully consistent with it.
(B) The GENERATED_RESPONSE is a superset of the EXPECTED_RESPONSE and is fully consistent with it.
(C) The GENERATED_RESPONSE contains all the same details as the EXPECTED_RESPONSE.
(D) There is a disagreement between the GENERATED_RESPONSE and the EXPECTED_RESPONSE.
(E) The answers differ, but these differences don't matter from the perspective of factuality.
Give your answer in the format "Answer: One of ABCDE, Explanation: ".
Your actual task:
QUESTION: {input_query}
GENERATED_RESPONSE: {generated_answer}
EXPECTED_RESPONSE: {expected_answer}
"""
input_query = (
"What are the top 5 topics that were explained? Only list succinct bullet points."
)
generated_answer = """
Here are the top 5 topics that were explained in the documentation for Torchtune:
* What is LoRA and how does it work?
* Fine-tuning with LoRA: memory savings and parameter-efficient finetuning
* Running a LoRA finetune with Torchtune: overview and recipe
* Experimenting with different LoRA configurations: rank, alpha, and attention modules
* LoRA finetuning
"""
expected_answer = """LoRA"""
dataset_rows = [
{
"input_query": input_query,
"generated_answer": generated_answer,
"expected_answer": expected_answer,
},
]
scoring_params = {
"llm-as-judge::base": {
"judge_model": judge_model_id,
"prompt_template": JUDGE_PROMPT,
"type": "llm_as_judge",
"judge_score_regexes": ["Answer: (A|B|C|D|E)"],
},
"basic::subset_of": None,
"braintrust::factuality": None,
}
response = client.scoring.score(
input_rows=dataset_rows, scoring_functions=scoring_params
)
Running Evaluations via CLI
The following examples give the quick steps to start running evaluations using the llama-stack-client CLI.
Benchmark Evaluation CLI
Usage: There are 2 inputs necessary for running a benchmark eval
eval-task-id: the identifier associated with the eval task. EachEvalTaskis parametrized bydataset_id: the identifier associated with the dataset.List[scoring_function_id]: list of scoring function identifiers.
eval-task-config: specifies the configuration of the model / agent to evaluate on.
llama-stack-client eval run_benchmark <eval-task-id> \
--eval-task-config ~/eval_task_config.json \
--visualize
Application Evaluation CLI
Usage: For running application evals, you will already have available datasets in hand from your application. You will need to specify:
scoring-fn-id: List of ScoringFunction identifiers you wish to use to run on your application.Datasetused for evaluation:- (1)
--dataset-path: path to local file system containing datasets to run evaluation on - (2)
--dataset-id: pre-registered dataset in Llama Stack
- (1)
- (Optional)
--scoring-params-config: optionally parameterize scoring functions with custom params (e.g.judge_prompt,judge_model,parsing_regexes).
llama-stack-client eval run_scoring <scoring_fn_id_1> <scoring_fn_id_2> ... <scoring_fn_id_n>
--dataset-path <path-to-local-dataset> \
--output-dir ./
Defining EvalTaskConfig
The EvalTaskConfig are user specified config to define:
EvalCandidateto run generation on:ModelCandidate: The model will be used for generation through LlamaStack /inference API.AgentCandidate: The agentic system specified by AgentConfig will be used for generation through LlamaStack /agents API.
- Optionally scoring function params to allow customization of scoring function behaviour. This is useful to parameterize generic scoring functions such as LLMAsJudge with custom
judge_model/judge_prompt.
Example Benchmark EvalTaskConfig
{
"type": "benchmark",
"eval_candidate": {
"type": "model",
"model": "Llama3.2-3B-Instruct",
"sampling_params": {
"strategy": {
"type": "greedy",
},
"max_tokens": 0,
"repetition_penalty": 1.0
}
}
}
Example Application EvalTaskConfig
{
"type": "app",
"eval_candidate": {
"type": "model",
"model": "Llama3.1-405B-Instruct",
"sampling_params": {
"strategy": {
"type": "greedy",
},
"max_tokens": 0,
"repetition_penalty": 1.0
}
},
"scoring_params": {
"llm-as-judge::llm_as_judge_base": {
"type": "llm_as_judge",
"judge_model": "meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
"prompt_template": "Your job is to look at a question, a gold target ........",
"judge_score_regexes": [
"(A|B|C)"
]
}
}
}