* docker compose ollama * comment * update compose file * readme for distributions * readme * move distribution folders * move distribution/templates to distributions/ * rename * kill distribution/templates * readme * readme * build/developer cookbook/new api provider * developer cookbook * readme * readme * [bugfix] fix case for agent when memory bank registered without specifying provider_id (#264) * fix case where memory bank is registered without provider_id * memory test * agents unit test * Add an option to not use elastic agents for meta-reference inference (#269) * Allow overridding checkpoint_dir via config * Small rename * Make all methods `async def` again; add completion() for meta-reference (#270) PR #201 had made several changes while trying to fix issues with getting the stream=False branches of inference and agents API working. As part of this, it made a change which was slightly gratuitous. Namely, making chat_completion() and brethren "def" instead of "async def". The rationale was that this allowed the user (within llama-stack) of this to use it as: ``` async for chunk in api.chat_completion(params) ``` However, it causes unnecessary confusion for several folks. Given that clients (e.g., llama-stack-apps) anyway use the SDK methods (which are completely isolated) this choice was not ideal. Let's revert back so the call now looks like: ``` async for chunk in await api.chat_completion(params) ``` Bonus: Added a completion() implementation for the meta-reference provider. Technically should have been another PR :) * Improve an important error message * update ollama for llama-guard3 * Add vLLM inference provider for OpenAI compatible vLLM server (#178) This PR adds vLLM inference provider for OpenAI compatible vLLM server. * Create .readthedocs.yaml Trying out readthedocs * Update event_logger.py (#275) spelling error * vllm * build templates * delete templates * tmp add back build to avoid merge conflicts * vllm * vllm --------- Co-authored-by: Ashwin Bharambe <ashwin.bharambe@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Ashwin Bharambe <ashwin@meta.com> Co-authored-by: Yuan Tang <terrytangyuan@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: raghotham <rsm@meta.com> Co-authored-by: nehal-a2z <nehal@coderabbit.ai>
11 KiB
Building a Llama Stack Distribution
This guide will walk you through the steps to get started with building a Llama Stack distributiom from scratch with your choice of API providers. Please see the Getting Started Guide if you just want the basic steps to start a Llama Stack distribution.
Step 1. Build
In the following steps, imagine we'll be working with a Meta-Llama3.1-8B-Instruct model. We will name our build 8b-instruct to help us remember the config. We will start build our distribution (in the form of a Conda environment, or Docker image). In this step, we will specify:
name: the name for our distribution (e.g.8b-instruct)image_type: our build image type (conda | docker)distribution_spec: our distribution specs for specifying API providersdescription: a short description of the configurations for the distributionproviders: specifies the underlying implementation for serving each API endpointimage_type:conda|dockerto specify whether to build the distribution in the form of Docker image or Conda environment.
At the end of build command, we will generate <name>-build.yaml file storing the build configurations.
After this step is complete, a file named <name>-build.yaml will be generated and saved at the output file path specified at the end of the command.
Building from scratch
- For a new user, we could start off with running
llama stack buildwhich will allow you to a interactively enter wizard where you will be prompted to enter build configurations.
llama stack build
Running the command above will allow you to fill in the configuration to build your Llama Stack distribution, you will see the following outputs.
> Enter an unique name for identifying your Llama Stack build distribution (e.g. my-local-stack): 8b-instruct
> Enter the image type you want your distribution to be built with (docker or conda): conda
Llama Stack is composed of several APIs working together. Let's configure the providers (implementations) you want to use for these APIs.
> Enter the API provider for the inference API: (default=meta-reference): meta-reference
> Enter the API provider for the safety API: (default=meta-reference): meta-reference
> Enter the API provider for the agents API: (default=meta-reference): meta-reference
> Enter the API provider for the memory API: (default=meta-reference): meta-reference
> Enter the API provider for the telemetry API: (default=meta-reference): meta-reference
> (Optional) Enter a short description for your Llama Stack distribution:
Build spec configuration saved at ~/.conda/envs/llamastack-my-local-llama-stack/8b-instruct-build.yaml
Ollama (optional)
If you plan to use Ollama for inference, you'll need to install the server via these instructions.
Building from templates
- To build from alternative API providers, we provide distribution templates for users to get started building a distribution backed by different providers.
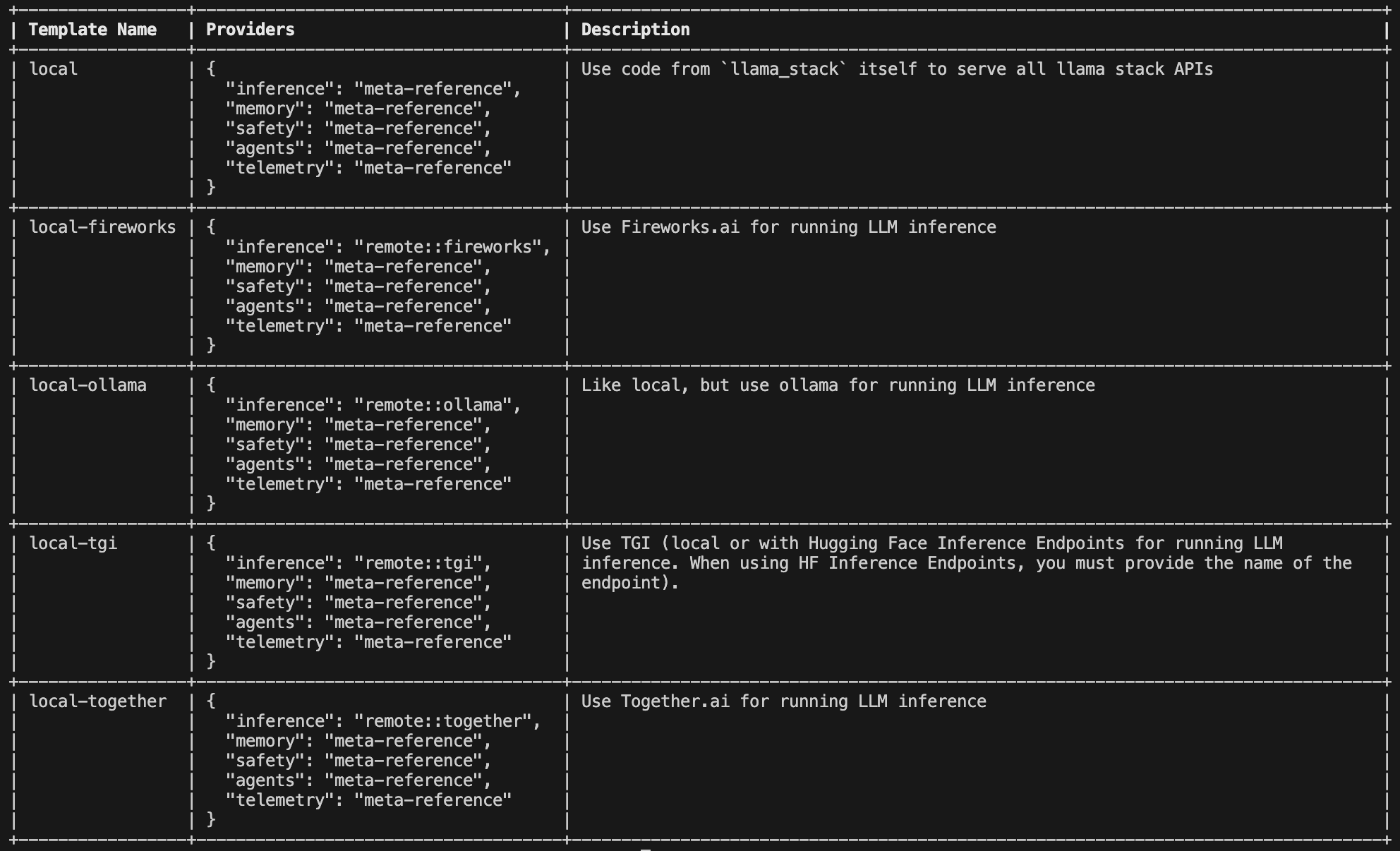
The following command will allow you to see the available templates and their corresponding providers.
llama stack build --list-templates
You may then pick a template to build your distribution with providers fitted to your liking.
llama stack build --template local-tgi --name my-tgi-stack
$ llama stack build --template local-tgi --name my-tgi-stack
...
...
Build spec configuration saved at ~/.conda/envs/llamastack-my-tgi-stack/my-tgi-stack-build.yaml
You may now run `llama stack configure my-tgi-stack` or `llama stack configure ~/.conda/envs/llamastack-my-tgi-stack/my-tgi-stack-build.yaml`
Building from config file
-
In addition to templates, you may customize the build to your liking through editing config files and build from config files with the following command.
-
The config file will be of contents like the ones in
llama_stack/distributions/templates/.
$ cat llama_stack/distribution/templates/local-ollama-build.yaml
name: local-ollama
distribution_spec:
description: Like local, but use ollama for running LLM inference
providers:
inference: remote::ollama
memory: meta-reference
safety: meta-reference
agents: meta-reference
telemetry: meta-reference
image_type: conda
llama stack build --config llama_stack/distribution/templates/local-ollama-build.yaml
How to build distribution with Docker image
Tip
Podman is supported as an alternative to Docker. Set
DOCKER_BINARYtopodmanin your environment to use Podman.
To build a docker image, you may start off from a template and use the --image-type docker flag to specify docker as the build image type.
llama stack build --template local --image-type docker --name docker-0
Alternatively, you may use a config file and set image_type to docker in our <name>-build.yaml file, and run llama stack build <name>-build.yaml. The <name>-build.yaml will be of contents like:
name: local-docker-example
distribution_spec:
description: Use code from `llama_stack` itself to serve all llama stack APIs
docker_image: null
providers:
inference: meta-reference
memory: meta-reference-faiss
safety: meta-reference
agentic_system: meta-reference
telemetry: console
image_type: docker
The following command allows you to build a Docker image with the name <name>
llama stack build --config <name>-build.yaml
Dockerfile created successfully in /tmp/tmp.I0ifS2c46A/DockerfileFROM python:3.10-slim
WORKDIR /app
...
...
You can run it with: podman run -p 8000:8000 llamastack-docker-local
Build spec configuration saved at ~/.llama/distributions/docker/docker-local-build.yaml
Step 2. Configure
After our distribution is built (either in form of docker or conda environment), we will run the following command to
llama stack configure [ <name> | <docker-image-name> | <path/to/name.build.yaml>]
- For
condaenvironments: <path/to/name.build.yaml> would be the generated build spec saved from Step 1. - For
dockerimages downloaded from Dockerhub, you could also use as the argument.- Run
docker imagesto check list of available images on your machine.
- Run
$ llama stack configure 8b-instruct
Configuring API: inference (meta-reference)
Enter value for model (existing: Meta-Llama3.1-8B-Instruct) (required):
Enter value for quantization (optional):
Enter value for torch_seed (optional):
Enter value for max_seq_len (existing: 4096) (required):
Enter value for max_batch_size (existing: 1) (required):
Configuring API: memory (meta-reference-faiss)
Configuring API: safety (meta-reference)
Do you want to configure llama_guard_shield? (y/n): y
Entering sub-configuration for llama_guard_shield:
Enter value for model (default: Llama-Guard-3-1B) (required):
Enter value for excluded_categories (default: []) (required):
Enter value for disable_input_check (default: False) (required):
Enter value for disable_output_check (default: False) (required):
Do you want to configure prompt_guard_shield? (y/n): y
Entering sub-configuration for prompt_guard_shield:
Enter value for model (default: Prompt-Guard-86M) (required):
Configuring API: agentic_system (meta-reference)
Enter value for brave_search_api_key (optional):
Enter value for bing_search_api_key (optional):
Enter value for wolfram_api_key (optional):
Configuring API: telemetry (console)
YAML configuration has been written to ~/.llama/builds/conda/8b-instruct-run.yaml
After this step is successful, you should be able to find a run configuration spec in ~/.llama/builds/conda/8b-instruct-run.yaml with the following contents. You may edit this file to change the settings.
As you can see, we did basic configuration above and configured:
- inference to run on model
Meta-Llama3.1-8B-Instruct(obtained fromllama model list) - Llama Guard safety shield with model
Llama-Guard-3-1B - Prompt Guard safety shield with model
Prompt-Guard-86M
For how these configurations are stored as yaml, checkout the file printed at the end of the configuration.
Note that all configurations as well as models are stored in ~/.llama
Step 3. Run
Now, let's start the Llama Stack Distribution Server. You will need the YAML configuration file which was written out at the end by the llama stack configure step.
llama stack run 8b-instruct
You should see the Llama Stack server start and print the APIs that it is supporting
$ llama stack run 8b-instruct
> initializing model parallel with size 1
> initializing ddp with size 1
> initializing pipeline with size 1
Loaded in 19.28 seconds
NCCL version 2.20.5+cuda12.4
Finished model load YES READY
Serving POST /inference/batch_chat_completion
Serving POST /inference/batch_completion
Serving POST /inference/chat_completion
Serving POST /inference/completion
Serving POST /safety/run_shield
Serving POST /agentic_system/memory_bank/attach
Serving POST /agentic_system/create
Serving POST /agentic_system/session/create
Serving POST /agentic_system/turn/create
Serving POST /agentic_system/delete
Serving POST /agentic_system/session/delete
Serving POST /agentic_system/memory_bank/detach
Serving POST /agentic_system/session/get
Serving POST /agentic_system/step/get
Serving POST /agentic_system/turn/get
Listening on :::5000
INFO: Started server process [453333]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://[::]:5000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Note
Configuration is in
~/.llama/builds/local/conda/8b-instruct-run.yaml. Feel free to increasemax_seq_len.
Important
The "local" distribution inference server currently only supports CUDA. It will not work on Apple Silicon machines.
Tip
You might need to use the flag
--disable-ipv6to Disable IPv6 support
This server is running a Llama model locally.
Step 4. Test with Client
Once the server is setup, we can test it with a client to see the example outputs.
cd /path/to/llama-stack
conda activate <env> # any environment containing the llama-stack pip package will work
python -m llama_stack.apis.inference.client localhost 5000
This will run the chat completion client and query the distribution’s /inference/chat_completion API.
Here is an example output:
User>hello world, write me a 2 sentence poem about the moon
Assistant> Here's a 2-sentence poem about the moon:
The moon glows softly in the midnight sky,
A beacon of wonder, as it passes by.
Similarly you can test safety (if you configured llama-guard and/or prompt-guard shields) by:
python -m llama_stack.apis.safety.client localhost 5000
Check out our client SDKs for connecting to Llama Stack server in your preferred language, you can choose from python, node, swift, and kotlin programming languages to quickly build your applications.
You can find more example scripts with client SDKs to talk with the Llama Stack server in our llama-stack-apps repo.