5 KiB
Using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enables your applications to reference and recall information from previous interactions or external documents.
Llama Stack organizes the APIs that enable RAG into three layers:
- the lowermost APIs deal with raw storage and retrieval. These include Vector IO, KeyValue IO (coming soon) and Relational IO (also coming soon.)
- next is the "Rag Tool", a first-class tool as part of the Tools API that allows you to ingest documents (from URLs, files, etc) with various chunking strategies and query them smartly.
- finally, it all comes together with the top-level "Agents" API that allows you to create agents that can use the tools to answer questions, perform tasks, and more.
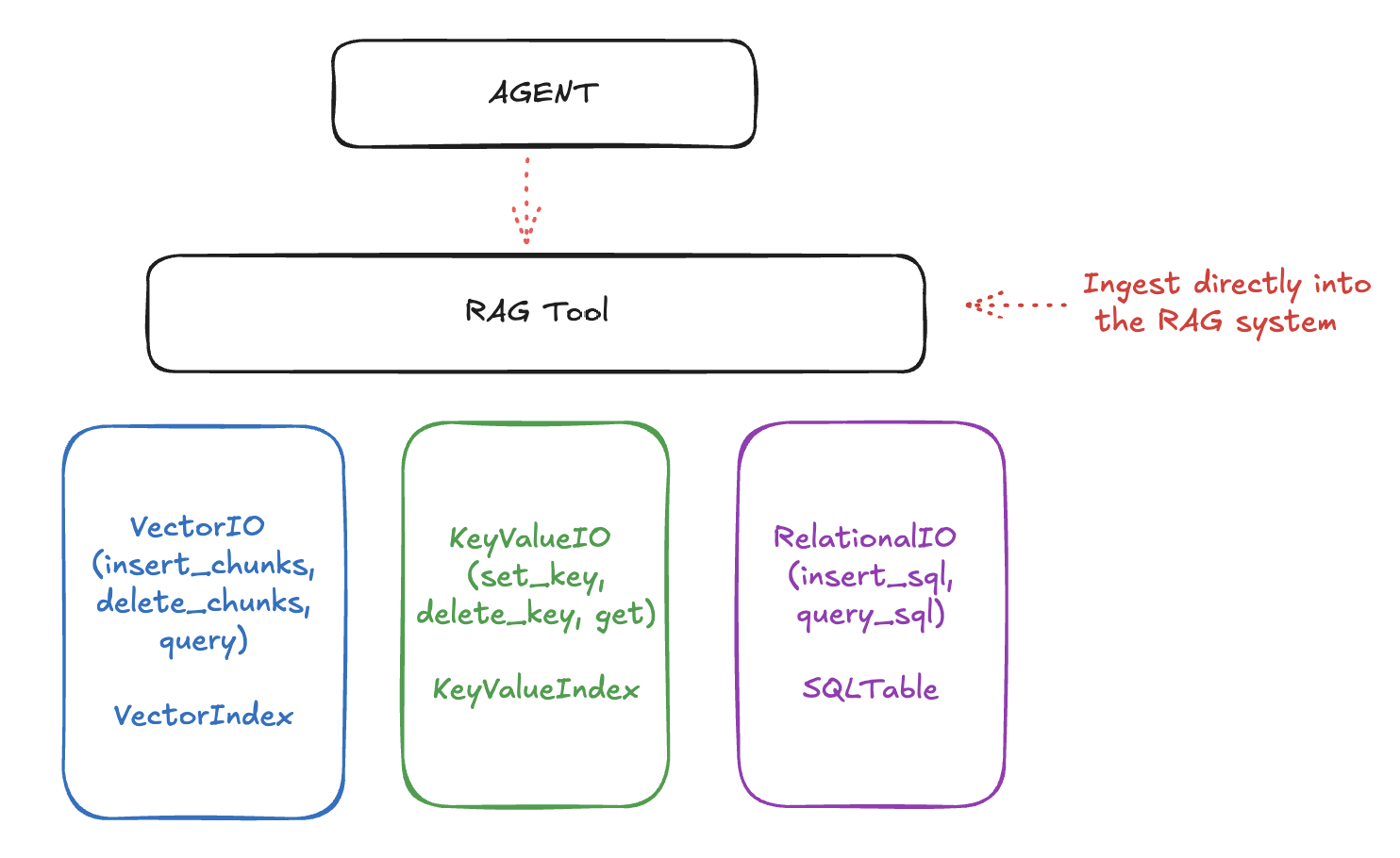
The RAG system uses lower-level storage for different types of data:
- Vector IO: For semantic search and retrieval
- Key-Value and Relational IO: For structured data storage
We may add more storage types like Graph IO in the future.
Setting up Vector DBs
Here's how to set up a vector database for RAG:
# Create http client
from llama_stack_client import LlamaStackClient
client = LlamaStackClient(base_url=f"http://localhost:{os.environ['LLAMA_STACK_PORT']}")
# Register a vector db
vector_db_id = "my_documents"
response = client.vector_dbs.register(
vector_db_id=vector_db_id,
embedding_model="all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
embedding_dimension=384,
provider_id="faiss",
)
# You can insert a pre-chunked document directly into the vector db
chunks = [
{
"document_id": "doc1",
"content": "Your document text here",
"mime_type": "text/plain",
},
]
client.vector_io.insert(vector_db_id=vector_db_id, chunks=chunks)
# You can then query for these chunks
chunks_response = client.vector_io.query(
vector_db_id=vector_db_id, query="What do you know about..."
)
Using the RAG Tool
A better way to ingest documents is to use the RAG Tool. This tool allows you to ingest documents from URLs, files, etc. and automatically chunks them into smaller pieces.
from llama_stack_client import RAGDocument
urls = ["memory_optimizations.rst", "chat.rst", "llama3.rst"]
documents = [
RAGDocument(
document_id=f"num-{i}",
content=f"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/torchtune/main/docs/source/tutorials/{url}",
mime_type="text/plain",
metadata={},
)
for i, url in enumerate(urls)
]
client.tool_runtime.rag_tool.insert(
documents=documents,
vector_db_id=vector_db_id,
chunk_size_in_tokens=512,
)
# Query documents
results = client.tool_runtime.rag_tool.query(
vector_db_ids=[vector_db_id],
content="What do you know about...",
)
Building RAG-Enhanced Agents
One of the most powerful patterns is combining agents with RAG capabilities. Here's a complete example:
from llama_stack_client import Agent
# Create agent with memory
agent = Agent(
client,
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct",
instructions="You are a helpful assistant",
tools=[
{
"name": "builtin::rag/knowledge_search",
"args": {
"vector_db_ids": [vector_db_id],
},
}
],
)
session_id = agent.create_session("rag_session")
# Ask questions about documents in the vector db, and the agent will query the db to answer the question.
response = agent.create_turn(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "How to optimize memory in PyTorch?"}],
session_id=session_id,
)
NOTE: the
instructionsfield in theAgentConfigcan be used to guide the agent's behavior. It is important to experiment with different instructions to see what works best for your use case.
You can also pass documents along with the user's message and ask questions about them.
# Initial document ingestion
response = agent.create_turn(
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "I am providing some documents for reference."}
],
documents=[
{
"content": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pytorch/torchtune/main/docs/source/tutorials/memory_optimizations.rst",
"mime_type": "text/plain",
}
],
session_id=session_id,
)
# Query with RAG
response = agent.create_turn(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What are the key topics in the documents?"}],
session_id=session_id,
)
You can print the response with below.
from llama_stack_client import AgentEventLogger
for log in AgentEventLogger().log(response):
log.print()
Unregistering Vector DBs
If you need to clean up and unregister vector databases, you can do so as follows:
# Unregister a specified vector database
vector_db_id = "my_vector_db_id"
print(f"Unregistering vector database: {vector_db_id}")
client.vector_dbs.unregister(vector_db_id=vector_db_id)
# Unregister all vector databases
for vector_db_id in client.vector_dbs.list():
print(f"Unregistering vector database: {vector_db_id.identifier}")
client.vector_dbs.unregister(vector_db_id=vector_db_id.identifier)